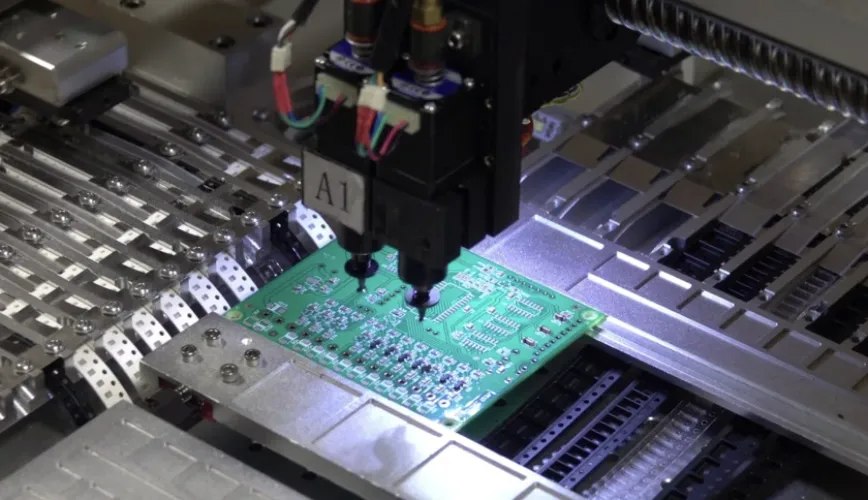
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly represents the pinnacle of modern electronics manufacturing, enabling the creation of compact, high-performance electronic devices that power our digital world.
Introduction to SMT Assembly
SMT assembly involves mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), eliminating the need for through-hole mounting in most applications. This technology enables:
- Higher component density
- Improved electrical performance
- Reduced manufacturing costs
- Enhanced reliability
SMT Assembly Process Flow
1. Solder Paste Application
The process begins with precise solder paste application using stencils:
Stencil Design Considerations:
- Aperture size optimization
- Paste release characteristics
- Registration accuracy
- Cleaning requirements
Process Parameters:
- Squeegee pressure: 2-4 kg/cm
- Print speed: 10-25 mm/s
- Separation speed: 0.5-3 mm/s
- Snap-off distance: 0-2 mm
2. Component Placement
High-speed pick-and-place machines position components with exceptional accuracy:
Placement Accuracy:
- Standard components: ±50μm
- Fine pitch components: ±25μm
- Ultra-fine pitch: ±15μm
Component Types:
- Resistors and capacitors (0201, 0402, 0603, 0805)
- Integrated circuits (QFN, BGA, CSP)
- Connectors and mechanical components
3. Reflow Soldering
The reflow process creates permanent solder joints through controlled heating:
Temperature Profile Zones:
- Preheat: 150-180°C (60-120 seconds)
- Thermal Soak: 150-200°C (60-120 seconds)
- Reflow: 230-250°C (30-90 seconds)
- Cooling: <6°C/second cooling rate
Advanced SMT Technologies
Fine Pitch Components
Modern electronics demand increasingly fine pitch components:
0.4mm Pitch QFP:
- Stencil thickness: 0.1-0.12mm
- Aperture ratio: 0.8-0.9
- Placement accuracy: ±25μm
0.3mm Pitch BGA:
- Solder ball diameter: 0.2-0.25mm
- Pad size: 0.2mm
- Via-in-pad technology required
System-in-Package (SiP)
SiP technology enables multiple functions in a single package:
- Heterogeneous integration
- Reduced form factor
- Improved performance
- Lower power consumption
Quality Control in SMT Assembly
Solder Paste Inspection (SPI)
Real-time inspection of solder paste deposits:
- Volume accuracy: ±10%
- Height uniformity: ±25μm
- Shape analysis: Area ratio >0.6
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Post-placement and post-reflow inspection:
- Component presence/absence
- Polarity verification
- Solder joint quality
- Dimensional accuracy
In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
Electrical verification of assembled boards:
- Continuity testing
- Component value verification
- Short circuit detection
- Functional testing
Process Optimization Techniques
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Continuous monitoring of key parameters:
- Placement accuracy trends
- Solder paste volume consistency
- Temperature profile stability
- Defect rate tracking
Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Optimizing designs for SMT assembly:
- Component orientation standardization
- Adequate spacing for inspection
- Thermal balancing considerations
- Test point accessibility
Common SMT Defects and Solutions
Solder Joint Defects
| Defect Type | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient Solder | Low paste volume | Optimize stencil design |
| Solder Bridges | Excessive paste | Reduce aperture size |
| Tombstoning | Thermal imbalance | Adjust pad design |
| Head-in-Pillow | Oxidation | Improve storage conditions |
Component Placement Issues
Misalignment:
- Root cause: Machine calibration
- Solution: Regular maintenance and calibration
Missing Components:
- Root cause: Feeder issues
- Solution: Preventive maintenance program
Industry 4.0 in SMT Assembly
Smart Manufacturing
Integration of IoT and AI technologies:
- Real-time process monitoring
- Predictive maintenance
- Automated quality control
- Data-driven optimization
Traceability Systems
Complete product lifecycle tracking:
- Component genealogy
- Process parameter recording
- Quality data correlation
- Rapid issue resolution
Environmental Considerations
Lead-Free Soldering
RoHS compliance requirements:
- SAC305 alloy (Sn96.5/Ag3.0/Cu0.5)
- Higher reflow temperatures
- Improved flux chemistry
- Enhanced process control
Energy Efficiency
Sustainable manufacturing practices:
- Optimized reflow profiles
- Energy recovery systems
- Reduced material waste
- Eco-friendly cleaning processes
Future Trends in SMT Assembly
Emerging Technologies
Embedded Components:
- Components within PCB substrate
- Reduced assembly complexity
- Improved electrical performance
3D Packaging:
- Vertical integration
- Through-silicon vias (TSV)
- Wafer-level packaging
Market Drivers
- 5G communication requirements
- Automotive electrification
- IoT device proliferation
- Miniaturization demands
Conclusion
SMT assembly continues to evolve, driven by the demands of modern electronics. Success requires:
- Advanced equipment capabilities
- Rigorous process control
- Continuous improvement mindset
- Investment in technology
At Highleap PCB, we combine state-of-the-art SMT assembly capabilities with decades of experience to deliver exceptional results for our customers across all industries.
Ready to optimize your SMT assembly process? Contact our engineering team for a comprehensive consultation on your next project.