When PCB designs fail electromagnetic compatibility testing or experience premature failures in the field, the root cause often traces back to fundamental design rule violations. IPC-2221 PCB design standards establish the foundation for reliable printed circuit board layouts, defining critical requirements for conductor spacing, current carrying capacity, thermal management, and material selection. These standards serve as the cornerstone for PCB design across industries, providing engineers with proven guidelines that ensure electrical performance, mechanical reliability, and manufacturing consistency.
At HILPCB, we manufacture PCBs in strict compliance with IPC-2221 standards, ensuring every board meets the established requirements for conductor geometry, spacing, and thermal performance. Our design review process validates adherence to IPC-2221 guidelines before fabrication, preventing costly design iterations and ensuring optimal performance from prototype through production.
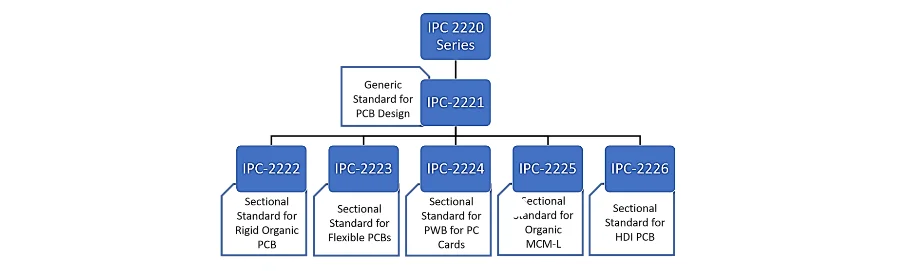
Understanding IPC-2221 PCB Design Standard Structure
IPC-2221 PCB standard provides comprehensive guidelines for printed circuit board design, covering everything from basic material requirements to complex thermal and electrical considerations. The standard is organized into logical sections that address different aspects of PCB design, making it an essential reference for engineers working on any electronic product.
Scope and Application of IPC-2221: The standard applies to rigid and flexible printed boards, covering single-layer through complex multilayer PCB designs. It establishes minimum design requirements that ensure manufacturability, reliability, and performance across diverse applications and operating environments.
Design Classes and Requirements: IPC-2221 defines three design classes with increasing levels of performance and reliability requirements. Class 1 provides general electronic products requirements, Class 2 addresses dedicated service electronic products, and Class 3 covers high-performance electronic products requiring continuous operation and extended life.
Material Specifications: The standard references appropriate base materials including FR4 PCB substrates, high-Tg PCB materials for elevated temperature applications, and specialized substrates for specific performance requirements. Material selection directly impacts the applicability of spacing and current-carrying capacity guidelines.
Environmental Considerations: IPC-2221 addresses environmental factors including operating temperature ranges, humidity conditions, and altitude effects that influence design requirements. These considerations ensure PCB designs remain functional across their intended operating conditions.
Conductor Width and Current Carrying Capacity Requirements
One of the most critical aspects of IPC-2221 PCB design involves determining appropriate conductor widths based on current requirements and allowable temperature rise. These calculations ensure traces can handle specified currents without exceeding safe operating temperatures.
Current Carrying Capacity Calculations
The standard provides detailed equations and charts for calculating conductor width based on several key parameters.
1. Internal Layer Conductor Sizing
For internal conductors in multilayer PCB designs, heat dissipation is constrained by surrounding dielectric layers. IPC-2221 provides specific charts and equations that account for reduced thermal dissipation in internal layers, typically requiring wider conductors for equivalent current carrying capacity compared to external layers.
- Temperature Rise Calculations: Standard equations account for conductor thickness, ambient temperature, and acceptable temperature rise
- Cross-Sectional Area Requirements: Minimum conductor cross-sections based on current density limits
- Thermal Modeling: Heat transfer considerations for internal conductors surrounded by dielectric materials
2. External Layer Conductor Design
External conductors benefit from better heat dissipation to ambient air, allowing higher current densities for equivalent temperature rise. The standard provides separate calculations for external layer conductors, accounting for improved thermal performance.
- Air Convection Effects: Enhanced heat dissipation for external conductors
- Surface Area Considerations: Impact of conductor width and thickness on thermal performance
- Environmental Factors: Ambient temperature and air circulation effects on current capacity
3. High-Current Applications
For power delivery applications requiring heavy copper PCB construction, IPC-2221 provides guidance on conductor design with enhanced copper thickness. These applications require special consideration of thermal management and mechanical stress.
Spacing Requirements and Electrical Clearance Guidelines
IPC-2221 PCB spacing requirements ensure adequate electrical isolation between conductors operating at different potentials, preventing breakdown, arcing, and interference that could compromise circuit operation or safety.
Conductor Spacing by Voltage: The standard establishes minimum spacing requirements based on operating voltage between conductors. These requirements consider both steady-state and transient voltage conditions, ensuring adequate safety margins under all operating conditions. Spacing requirements increase significantly with voltage, particularly above 50V where additional safety considerations apply.
Environmental Category Impact: Operating environment significantly affects spacing requirements. The standard defines different environmental categories including controlled indoor environments, harsh industrial conditions, and outdoor exposure scenarios. Each category requires different minimum spacing values to account for contamination, moisture, and other factors that could reduce insulation effectiveness.
Altitude Derating: Air density decreases with altitude, reducing the dielectric strength of air gaps between conductors. IPC-2221 provides derating factors for high-altitude applications, requiring increased spacing to maintain equivalent breakdown voltage performance.
Coated vs. Uncoated Surfaces: Conformal coatings can significantly reduce spacing requirements by providing additional insulation. The standard provides guidance on spacing reduction factors for various coating types and thicknesses, enabling more compact designs when appropriate protective coatings are applied.
Via Design and Interconnection Standards
Via design represents a critical aspect of IPC-2221 PCB requirements, affecting both electrical performance and mechanical reliability. Proper via design ensures reliable layer-to-layer connections throughout the board's operational lifetime.
Via Size and Aspect Ratio Limits: The standard establishes maximum aspect ratios (board thickness to via diameter ratio) to ensure reliable plating and minimize the risk of barrel cracking or plating voids. These limits vary based on board thickness and manufacturing capabilities, with stricter requirements for HDI PCB designs using microvias.
Annular Ring Requirements: Minimum annular ring sizes ensure adequate connection area between vias and pads, accounting for drilling and registration tolerances during manufacturing. IPC-2221 specifies different annular ring requirements based on via type and design class, with tighter requirements for higher reliability applications.
Via Fill and Plugging Guidelines: The standard addresses various via treatment options including open vias, plugged vias, and filled vias. Each approach has specific design requirements and manufacturing considerations that affect electrical performance and mechanical reliability.
Thermal Via Design: For applications requiring enhanced thermal performance, IPC-2221 provides guidance on thermal via arrays and design strategies that maximize heat transfer between layers. These considerations are particularly important in high thermal PCB applications.
HILPCB — IPC-2221 Compliant PCB Manufacturing Excellence
1. Our IPC-2221 Expertise
We specialize in manufacturing PCBs that fully comply with IPC-2221 design standards, ensuring every board meets the established requirements for reliability, performance, and manufacturability. Our engineering team provides comprehensive design review services that validate adherence to IPC-2221 guidelines, identifying potential issues before fabrication and preventing costly design revisions.
2. Our IPC-2221 Capabilities
- Design Rule Verification — Automated checking of spacing, width, and via requirements against IPC-2221 standards
- Current Carrying Capacity Analysis — Thermal modeling and conductor sizing validation per standard requirements
- Material Compliance — Complete material traceability and certification to IPC-2221 specifications
- Large Volume Assembly — Production scaling with consistent IPC-2221 compliance
- Multi-layer Stackup Design — Optimized layer arrangements that meet standard requirements while minimizing cost
3. Why Choose HILPCB for IPC-2221 PCB Manufacturing
- Standards Compliance — Complete adherence to IPC-2221 requirements with documentation and traceability
- Design Support — Engineering assistance to ensure designs meet standard requirements before fabrication
- Quality Assurance — Comprehensive testing and inspection procedures that validate standard compliance
- Manufacturing Excellence — Advanced processes that consistently deliver IPC-2221 compliant PCBs
From initial design review through volume production, we ensure your PCBs meet all IPC-2221 requirements for electrical performance, mechanical reliability, and manufacturing consistency. Our comprehensive approach eliminates design risks and ensures successful product launches with reliable, standards-compliant PCBs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between IPC-2221 design classes? Class 1 provides general requirements for commercial products, Class 2 covers dedicated service applications requiring higher reliability, and Class 3 addresses high-performance applications requiring continuous operation and extended life.
Q: How do I calculate trace width using IPC-2221 standards? IPC-2221 provides charts and equations based on current requirements, acceptable temperature rise, conductor thickness, and layer position (internal vs. external). The standard includes specific calculation methods for different scenarios.
Q: What are the minimum spacing requirements in IPC-2221? Spacing requirements depend on operating voltage, environmental category, and altitude. The standard provides detailed tables with minimum spacing values for different voltage ranges and operating conditions.
Q: Does IPC-2221 apply to flexible PCBs? Yes, IPC-2221 covers both rigid and flexible printed circuit boards, though flex PCB designs may have additional considerations covered in IPC-2223.
Q: How often is IPC-2221 updated? IPC standards are periodically reviewed and updated to reflect technological advances and industry feedback. The current revision incorporates modern materials and manufacturing processes.
Q: Can IPC-2221 requirements be modified for specific applications? While IPC-2221 provides baseline requirements, specific applications may require additional constraints or modified requirements based on performance, environmental, or reliability needs.

